Rosacea – Symptoms, Causes, And Treatment
Written by Sai Pragna Chagarla, Writer at Hola Health
Medically reviewed by Dr Nelson Lau, MBBS FRACGP, GP & Digital Health Specialist


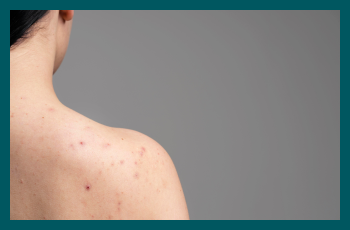
Rosacea is a prevalent skin condition that affects people worldwide, especially women between the ages of 30 and 50 years. As a chronic disorder characterised by facial redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes pustules, rosacea can have a significant impact on individuals’ physical and emotional well-being.
Australia’s diverse climate and environmental conditions can pose unique challenges for individuals with rosacea. The country’s high levels of ultraviolet (UV) radiation, combined with hot temperatures, can act as triggers for rosacea flare-ups. Prolonged sun exposure, common in Australia due to its outdoor lifestyle, can exacerbate redness and inflammation. Moreover, factors such as wind, humidity, and sudden temperature changes can contribute to the development of rosacea symptoms. It is important to understand the various triggers of Rosacea to identify what might be causing the flare-ups in a particular person.
Types Of Rosacea
There are different types of Rosacea depending on where and how it occurs. The common 4 types that are seen are:
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR): There will be persistent facial redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels on the face.
- Papulopustular Rosacea (PPR): In addition to facial redness, individuals also experience acne-like bumps (papules and pustules) on the central part of the face.
- Ocular Rosacea: This affects the eyes, leading to a range of symptoms such as, Irritation, dryness, burning, grittiness, and redness
- Phymatous or Swollen Rosacea: The skin on the nose, chin etc hardens looking like an orange peel.
The National Rosacea Society Categorises Rosacea Symptoms Into Two Groups
- Primary category: Involves facial flushing, redness, visible blood vessels, papules, and pustules.
- Secondary category: Involves burning or stinging, swelling, ocular manifestations, dry appearance, or plaques.
Causes and Triggers of Rosacea:
The exact cause of rosacea remains unclear, but a combination of genetic, environmental, and vascular factors is believed to contribute to its development. Certain triggers can exacerbate rosacea symptoms, including:
- Genetics: Individuals with a family history of rosacea may be more predisposed to developing the condition.
- Demodex Mites: These tiny mites that inhabit facial skin are found in higher numbers in individuals with rosacea, though the nature of this relationship is still being researched.
- Abnormal Blood Vessels: Aberrations in blood vessels near the skin’s surface may contribute to the characteristic redness associated with rosacea.
- Immune System Dysfunction: An abnormal immune response may play a role in the development of rosacea.
- Hot weather, freezing weather or sunlight
- Spicy foods, alcohol, and other drinks
- Stressful environment, anger, exercise, certain medication and more
Rosacea Symptoms
Rosacea manifests in several ways, and its symptoms can range from mild to severe. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Facial Redness: Persistent redness, often resembling a sunburn, particularly on the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin.
- Visible Blood Vessels: Small, visible blood vessels (telangiectasia) may appear on the skin.
- Bumps and Pustules: Small, red, pus-filled bumps resembling acne may develop.
- Eye Irritation: Ocular symptoms, such as dryness, burning, and irritation, may occur in some individuals (ocular rosacea).
- Enlarged Nose: In rare cases, rhinophyma, a condition characterised by thickening of the skin and enlargement of the nose, may develop.
Rosacea Treatments
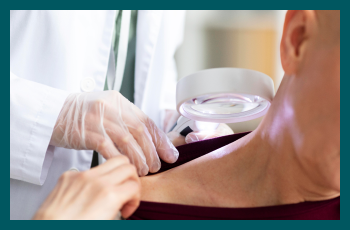
While there is no permanent cure for Rosacea, one should consider speaking to a doctor if they find one or more symptoms above. A proper treatment plan tailored to the specific symptoms and severity of the condition may be made along with your doctor.
Common Treatment Approaches Include:
- Topical medications or oral medications: This could be antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications.
- Laser Therapy to reduce the appearance of the blood vessels on the face and other parts with the condition.
- Avoiding triggers by maintaining a trigger diary
- Skincare Routine: Gentle skincare practices, including the use of mild cleansers and hypoallergenic moisturisers, can help manage symptoms.
- Sunscreen: Physical sunscreens containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are better for sensitive skin prone to rosacea
- Eye Care: Individuals with ocular rosacea may benefit from artificial tears, warm compresses, and other eye care measures.
Rosacea is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management, but with the right approach, individuals can achieve significant improvement in symptoms and maintain a good quality of life. Diagnosing the specific type of rosacea is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan. Speaking to a dermatologist or a general practitioner who will consider the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and physical examination when determining the most appropriate course of action is necessary in case of Rosacea. Additionally, raising awareness about the condition can help reduce the stigma associated with facial redness and encourage those affected to seek the support and treatment they need.

Consult an Online Doctor in 15 mins
- Speak to an Australian-registered health practitioner
- Telehealth appointment available 24 hours a day, all year round
- Request scripts, med certs, referrals or get medical advice


Consult an Online Doctor in 15 mins
- Speak to an Australian-registered health practitioner
- Telehealth appointment available 24 hours a day, all year round
- Request scripts, med certs, referrals or get medical advice
Reference
- Rosacea – Health Direct: Reference Link
- What is Rosacea – The Australian Society of Dermal Clinicians: Reference Link
- Standard classification of rosacea: Report of the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee on the Classification and Staging of Rosacea, National Rosacea Society : Reference Link
- Rosacea – The Australian College of Dermatologists: Reference Link
- Rosacea – Better Health Channel:Reference Link
- Rosacea – RACGP: Reference Link
Stay in the loop
for health updates & telehealth offers for first-time users.
[wpforms id="3450"]What we treat
- Cough
- Nausea & vomiting
- Fever
- Hayfever
- Fatigue
- Sore throat
- Acne
- Hair loss
- Gout
- Eczema
- Rosacea
- Sunburn
- UTI
- Erectile dysfunction
- Contraception
- Morning sickness
- Morning after pill
- Prostate health
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Stress
- Grief & loss
- Antidepressants
- Premature ejaculation
- Asthma
- Blood pressure
- Blood thinners
- Diabetes
- Cholesterol
- Migraines & headaches
- Allergies
- Body ache
- Heartburn & reflux
- Sleep disorder
- Smoking cessation
- Pain relief
- Gastro
Related Articles
Disclaimer
This content is created for informational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. Always seek the guidance of your doctor or other qualified health professional with any questions you may have regarding your health or a medical condition. For emergencies please immediately contact 000.


 Facebook
Facebook  X
X  Copy Link
Copy Link